ABS has been a very common name in the 3D printing industry. It’s very durable, heat-resistant, inexpensive, and simply available. However, a comparatively newer filament has proved to be a formidable challenger in terms of strength and warmth stability.
The new kid on the block, known as PETG, has quietly made its thanks to being one among the foremost popular filament materials today, next only to ABS and PLA.
PETG vs ABS: What are the Differences? How do ABS and PETG compare side-by-side? Is there a reason to settle on one over the other? Read on an in-depth comparison of these two 3D printing materials.
Contents
What is PETG
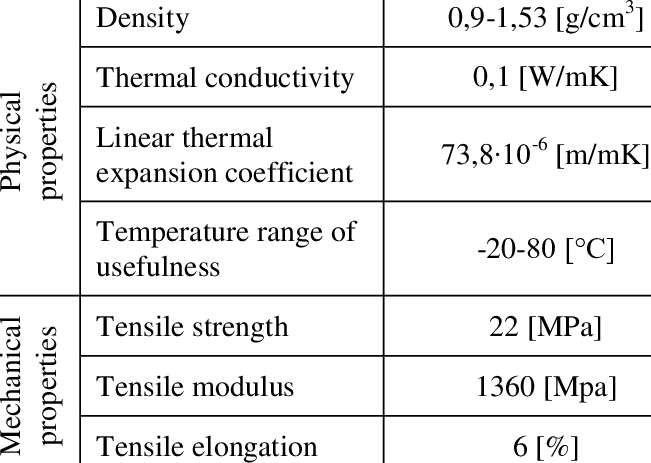
Polyethylene terephthalate glycol, commonly referred to as PETG or PET-G, is a thermoplastic polyester that is known for chemical resistance, durability, and excellent formability for manufacturing.
PETG is often easily vacuumed and pressure-formed also as heat-bent because of its low forming temperatures. This feature makes it exceptionally known for consumer and commercial applications that involve 3D printing, or other heat-forming manufacturing techniques.
Additionally, PETG is well-suited for fabrication techniques like die-cutting, bending, and routing.
Advantages of PETG
1. Better impact resistance
PETG has higher levels of flexibility and ductility compared to other polymers such as standard PET, ABS, and even PLA. This suggests that PETG is in a position to deform very slightly upon impact, giving it greater resistance to the sudden or sustained application of force. This is often one of its more unique characteristics and key property of PETG.
2. Not as susceptible to warping
PETG and ABS may both be high-temperature filaments, but their simple use properties are miles apart. The advantages of PETG are two-fold: not only is its shrinkage upon cooling much less pronounced, but it also has excellent layer adhesion.
PETG could also be less durable than ABS, but its multilayer adhesion feature somehow takes care of this problem. The extra strength of PETG prints products that won’t be easily affected by warping.
3. Doesn’t produce toxic odors while printing
A major reason why many 3D printing professionals have begun to shift from PETG to ABS is that the incontrovertible fact that PETG prints without releasing any unpleasant odor or toxic gases. This is often a big safety and health upgrade.
4. High chemical resistant
Standard PET is already quite the chemically-stable plastic, but the addition of glycol’s ring structure makes PETG impervious to a variety of acids, bases, and solvents. Prosthetic devices that are in constant contact with biological agents enjoy this level of stability.
5. Ideal for clear 3D prints
PETG is taken into account by many to the simplest filament for printing clear objects that permit the maximum amount of light as possible to penetrate through, even with minimal post-processing. This is often because PETG may be a naturally clear plastic – it is only through additives that it gains color.
The case for ABS is the exact opposite. ABS isn’t a transparent plastic and has got to be treated to become somewhat clear. Even with chemical additives and post-processing via vapor acetone bath.
Disadvantages of PETG
What is ABS?
ABS is an acronym in 3D that stands for Acetonitrile Butadiene Styrene, a terpolymer made from three different monomers. Each of those three monomers – acetonitrile, butadiene, and styrene – contribute a critical element that determines the physical and chemical properties of ABS.
These three monomers also can be mixed at different proportions which control which of the properties are most prevalent. With a singular combination of thermal stability, durability, and a glossy finish, ABS has quickly become one of the foremost widely used filament materials in 3D printing.
The extreme flexibility and versatility of ABS have also made it an important polymer for engineering. Most polymers made using ABS as a base are utilized in a good range of commercial and domestic or hobby applications.
From its conception as a viable replacement to rubber, ABS is now one among the highest-selling engineering thermoplastics.
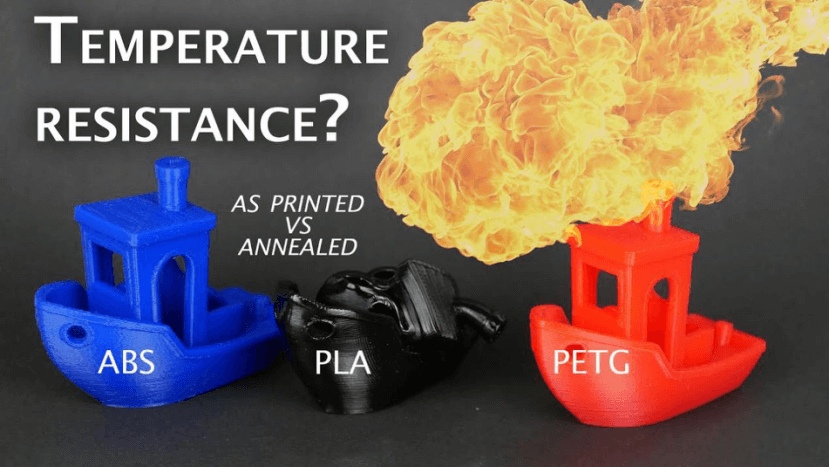
1. Resistance to high temperatures
ABS prints at a temperature range of 220 to 250 °C, which easily one among the very best temperature ranges needed for D printing. Although this makes printing with ABS very energy-intensive (and presents a couple of challenges within the printing process), it also makes ABS prints remarkably stable when exposed to heat.
This has made ABS a perfect material for items that are frequently exposed to high temperatures like the dashboard and seats of a car, or pipes and fittings for decent liquids.
2. Cheaper
In terms of producing costs, ABS isn’t that less expensive than PETG. However, ABS is far more widely used and more easily available. You will easily find cheap spools of ABS filament just because of the abundance of comparable products.
3. Better post-processing options
The compatibility of ABS with acetone as a solvent is one of its more unique characteristics. Not only is it possible to form an ABS glue by dissolving ABS in acetone, but acetone also can be used to smoothen an ABS print.
A method known as acetone vapor bath allows for a consistently smooth finish on an ABS print by exposing it to the fumes of acetone, which readily vaporize at high temperatures. Compare to other finishing methods, using an acetone vapor bath requires such a lot less effort but produces exceptional results.
4. Less hygroscopic
All 3D printing filaments are hygroscopic, which suggests that they readily take up moisture from the air. Between filaments, however, some are simply more hygroscopic than others. Comparing ABS with PETG, ABS may be a bit less susceptible to moisture intake, making it easier to handle and store.
Disadvantages of ABS for 3D Printing
1. Prints at very heat
The high-temperature characteristic of ABS could be desirable for the end-product, but it also means you’ll be using a lot of power during the printing. Granted that PETG prints only at slightly lower temperatures, but the difference can add up over many hours and really hurt your power bill.
2. Difficult to use
The high-temperature tolerance property of ABS makes it one among the foremost notoriously difficult filaments to work with. Not only does one need to deal with the standard challenges of printing at high temperatures (like stringing and “heat creep” within the extruder), but there’s also the very fact that ABS has poor layer adhesion and shrinks by a significant margin when it gets colder.
In terms of extracting your first layer to stay to the build platform, ABS might just be the foremost finicky filament. It has a high tendency to warp, making it necessary to use a heated bed with a strong adhesion aid like ABS glue or Kapton tape. You would possibly even got to resort to other measures, like printing a raft or brim on your project’s first layer or using a print chamber to hamper the cooling process further.
For these reasons, ABS isn’t exactly a filament we might consider beginner-friendly. The results are well worth the effort within the end, but there’s still with great care much effort involved.
3. Produces toxic fumes
Another distinct disadvantage of working with ABS is that it produces tons of styrene gas while printing. Not only is that this gas irritating and noxious, but it’s also a known carcinogenic. This suggests that you should never print with ABS in a room without ventilation. Even then, you do not want to remain within the same room as a 3D printer that’s extruding ABS.
Which Filament Should I Use? PETG vs ABS
As we have seen, PETG and ABS have different properties. So which one should I use? To answer this, there are several parameters that we can use to decide on the ideal filament for 3D printing:
You can print with PETG if:
1. You need something which will withstand more impact
The brittleness of ABS means it can easily shatter or crack when subjected to a robust impact. This is often not the case with PETG. When PETG experiences an impression, it can deform but essentially remains intact.
2. You’re printing a project for outdoor use
PETG has become an ideal 3D filament for companies who want to place up outdoor signages. Not only can PETG withstand the acute temperature of a sunny day, but it also doesn’t degrade with sustained exposure to UV radiation.
3. You don’t want to affect printing
PETG has often been known to be a filament that mixes the strength of ABS and therefore the simple use of PLA. It is more forgiving than ABS when it involves warping and layer adhesion and doesn’t release irritating and harmful odors.
You can use ABS if:
1. You need a filament that is more rigid and heat-resistant
ABS is an ideal container for handling boiling fluids and its rigidity means it acts as a far better protective barrier for its contents.
2. You would like to urge a smooth finish
It is undisputed fact that finishing an ABS print using an acetone vapor bath is, by far, the simplest way to do a smooth 3D printing project. It’s quick, doesn’t take tons of skill, and it takes little or no effort.
3. You want a cheap 3D filament
You will save a couple of dollars by sticking to ABS instead of PETG. The difference isn’t really that small, and we already see PETG and ABS filaments that are almost priced the same.
Conclusion
I hope that you have grasped some in-depth knowledge about ABS and PETG. You can now find the difference between these two types of 3D filaments.
In case you would like to use any of these two filaments for 3D printing, consider contacting a 3D printing service company for advice.
Related source links:
Related source links:
Handbook: Everything you need to know about PETG
PETG vs PLA: What are the Differences?
Polycarbonate vs Acrylic: What are the Differences?
Nylon vs Polyester: What are the Differences?
Trivex vs polycarbonate: What are the Differences?
White paper: The Complete Guide To thermoforming
Everything You Need to Know about PVC Pipe Sizes
Rocheindustry specializes in high quality rapid prototyping, rapid low-volume manufacturing and high-volume production. The services of rapid prototype we providing are professional Engineering, CNC Machining including CNC Milling and Turning, Sheet Metal Fabrication or Sheet Metal Prototyping, Die casting, metal stamping, Vacuum Casting, 3D printing, SLA, Plastic and Aluminum Extrusion Prototyping, Rapid Tooling, Rapid Injection Moulding, Surface Treatment finish services and other rapid prototyping China services please contact us now.