Contents
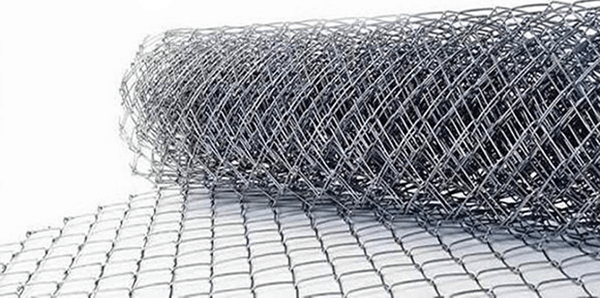
Galvanized Steel Overview
Galvanized steel is known for its reliability. This explains why it is used in a wide range of applications. Planning to use this metal? Then there are several things that you need to know about it. In this article, we are going to give you a complete guide for buying and using galvanized steel. If you are using plain steel and you would like it to be galvanized, we will show you how to get the job done.
What is Galvanized Steel?
To understand what galvanized steel, let’s look at the process that is used to create it. That is galvanization.
Hot Dip Galvanizing may be a unique process. When stainless steel is immersed into molten zinc, a series of zinc-iron alloy layers are formed through a metallurgical reaction between the iron and zinc, providing a durable coating that is an integral part of the steel.
When the chemical reaction between iron and zinc has virtually stopped, and therefore the item is extruded out of the galvanizing bath complete with its outer coating of free zinc, the method is complete.
Actually, there’s no demarcation between steel and zinc but a gradual transition through the series of alloy layers, which give the metallurgical bond.
Basically, galvanized steel is nothing but steel that has been coated with a layer of zinc. By placing the steel materials during a hot molten bath of zinc during a process called ‘hot-dip galvanization’, the two metals are permanently bound together, resulting in a more resistant version of the metal.
Brief History of Galvanizing
The history of galvanizing is traced back for more than 300 years ago. This was when an alchemist-come-chemist dreamt up a reason to immerse clean iron into molten zinc and to his shimmering silver coating developed onto the iron. This was to become the primary step within the genesis of the galvanizing process.
In 1836, Sorel in France took out several patents for this process of coating steel by dipping it in hot molten zinc after first cleaning it. He provided the method with its name ‘galvanizing’. It is interesting to notice that Sorel was conscious of the electrochemical nature of corrosion and, therefore, the role of the zinc coating on the iron.
Galvanized steel is all around us and plays an important role in our everyday lives. It utilized in construction, transport, agriculture, power transmission, and everywhere that good corrosion protection and long life are essential.
It, as an example, helps light our roads (lighting columns) and supply power for our homes, hospitals, and offices (high voltage pylons). Many other essential industries make use of galvanizing.
How is Steel Galvanized?
There are two main methods that are used for galvanizing steel. These are hot-dip galvanization, continuous galvanization.
Hot Deep Galvanization
Hot deep galvanization is the most common process that is used for galvanizing steel.
The hot-dip galvanizing mainly entails the process of submerging the steel into a molten zinc bath (approximately 680 degrees Fahrenheit). When the material is extruded from the zinc bath and cooled, a reaction to the oxygen within the air takes place. The reaction causes the zinc to become a part of the steel (an iron-zinc alloy bond). The new surface finish appears to possess a crystalline finish or spangled finish.
While this is often the foremost common sort of galvanization, it’s often used for steel products that have previously been fabricated because the thickness of the ultimate product isn’t easily controlled. This leads to an alternative method of the galvanization process which is known as continuous galvanizing.
Continuous Galvanization
Continuous galvanizing entails applying the zinc coating to the surface of an endless ribbon of steel (coil) because it passes through a zinc bath. The coil travels at speeds of roughly 600 feet per minute.
As the coil leaves the zinc bath, it carries with it an additional layer of molten zinc. The additional zinc is removed with high air (air knives) to make the specified thickness. The material is then allowed to chill, and therefore, the spangled finish is made.
Continuous galvanizing allows for more precise control of the thickness and is usually used for steel products that haven’t yet been fabricated. Because the coating thickness increases, the danger of losing some coating during fabrication or forming also increases.
Steel Galvanizing Process
Regardless of the type off galvanization, here are the steps that are followed when executing steel galvanization:
1. Cleaning: The steel metal is cleaned before it is taken through any other process. The cleaning is done in a degreasing solution. After cleaning, the still must be rinsed to get rid of the solution.
2. Pickling: The clean steel is pickled by being dipped in a solution of sulphuric acid.
3. Fluxing: The metal is then fluxed by being dipped inside the aqueous solution. In most cases, the solutions are zinc ammonium chloride.
4. Galvanization: The steel is galvanized by being immersed in molten zinc.
5. Inspection: The last stage entails inspecting the galvanized steel for consistency.
Here is an image of steel galvanization process
Image source https://galvanizeit.org/inspection-course/galvanizing-process
Why Galvanized Steel? Advantages
Whatever you want to do with the steel material, it is always advisable to go for the galvanized steel. Here are the top benefits of galvanized steel material:
Cheaper: galvanized steel costs lower compared to most treated steels. Additionally, galvanized steel is instantly able to be used when delivered. It doesn’t require additional preparation of the surface, inspections, painting/coatings, etc. sparing companies more costs on their end.
Longer life: With galvanization, a bit of commercial steel is predicted to last quite 50 years in average environments and may last for over 20 years with severe exposure to water and other harsh elements. There is no regular steel maintenance that is required. The immense durability of the steel’s finished product also increases the product’s reliability.
The sacrificial anode: ensures that the encompassing zinc coating protects any damaged steel. It doesn’t matter if a steel section is totally exposed; the zinc material will still corrode first. The coating will corrode before to the steel, creating sacrificial protection to the damaged sections of the steel.
Rust resistance: The iron elements in steel are incredibly susceptible to rusting, but the addition of zinc acts as a protective buffer or layer between the steel and any moisture or oxygen. Galvanized steel is extremely protective, including sharp corners and recesses that couldn’t be protected with other coatings, making it immune to damage.
Time-saving: How long does it take to have the steel galvanized? You may ask. The steel galvanization process can take the shortest time available. All you need is to find a company that provides steel galvanizing services. You will get the job done within a short time-frame.
Uses of Galvanized Steel? Applications
There are numerous applications of galvanized steel. If you spot a steel material, there is a high chance that it is galvanized.
Galvanized steel can be used for making components of both small and large machines. Here are the most common applications of galvanized steel.
Automotive industry Galvanized steel has been used on vehicles for many years. The utilization of zinc-coated bodies (galvanized steel) for automobiles is now the norm in the car manufacturing industry. The body component of a car makes up about 80% of the body, all using galvanized steel.
The rust -resistance of galvanized steel is additionally an honest marketing tool for the competitive automotive industry since it can provide ‘anti-rust warranties’ to the car buyers.
Construction and building industry Whether for residential or commercial, the sturdiness of galvanized steel has made it popular for over a century within the housing and construction industry. It is also selected for construction due to its aesthetics;
The ‘shine’ that galvanized steel provides gives it an up to date feel and is popular in modern architectural designs. Also, it isn’t just used for giant structural pieces but things like fencing, gutters, rails, tubing, poles, and far more.
Telecommunication industry Phone lines aren’t a simple maintenance job; they are very tall and sometimes difficult to succeed in. Hot-galvanized steel is often used on phone wiring and equipment boxes, which decreases the danger of injury while at the same time reduces the maintenance cost.
Farming Quite a good percentage of farm equipment are made of galvanized steel material. The numerous advantages that come with this type of steel make it suitable to survive unfriendly farm conditions.
Electric equipment and appliances Take a look at the electric appliances in your house. Is there anything that you can notice about their casing? Most of the cases for electric appliances are made of galvanized steel material. In fact, even some interior parts of the electric appliances are made of this steel.
Galvanized Steel Services in China-Roche Industry
Do you have some steel that you would want them galvanized? Consider getting the job done by the best-galvanized steel manufacturer in China. This is exactly what Roche Industry does.
We galvanize steel metals for different applications. All that you need is to contact us and we send you everything that you need to know about galvanized steel.
Rocheindustry specializes in high quality rapid prototyping, rapid low-volume manufacturing and high-volume production. The services of rapid prototype we providing are professional Engineering, CNC Machining including CNC Milling and Turning, Sheet Metal Fabrication or Sheet Metal Prototyping, Die casting, metal stamping, Vacuum Casting, 3D printing, SLA, Plastic and Aluminum Extrusion Prototyping, Rapid Tooling, Rapid Injection Moulding, Surface Treatment finish services and other rapid prototyping China services please contact us now.